

























 Bearings
ABN200
Bearings
ABN200
Bearings are indispensable machine elements that constrain motion and reduce friction between moving parts.
There are numerous grinding operations involved in the manufacturing of bearings, including face grinding. As large contact areas are involved in this process, an abrasion resistant grit with good thermal conductivity like cubic boron nitride (CBN) is the most appropriate material. Dulling of the grit would enlarge the contact area and increase the possibility of thermal damage to the workpiece.
Element Six ABN200 is the optimal choice in this application due to its self-sharpening capability - enabling prolonged tool life and reduced possibility of thermal damage to the work piece.
 CV Joint
DBS900
CV Joint
DBS900
A constant-velocity (CV) joint is typically attached to the ends of the drive shaft to allow transmission of rotation and power through variable angles. CV joints allow for effective vertical movement of the wheel over bumps, while still transmitting power.
Tools made of polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) material offer maximum process reliability and provide consistently high quality and accuracy for the hard machining of CV joints. Element Six has developed DBS900, a very high performance grade, that offers cost effective tooling solutions.
 Driveshaft
PureCut DHA650
Driveshaft
PureCut DHA650
The driveshaft is critical to effectively transmit the engine's power and torque to the driven wheels of the car. The wheels are typically some distance away from the output of the gearbox, attached to the engine; therefore a means of transmitting the power is vital. A hard material which resists torsion and shear stress is required - typically case hardened steel is used for long component life.
It is preferable to machine these parts in the hardened state to avoid deformations during the heat treatment process. Polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) was the enabling technology for hard part turning.
 Ring Gear
PureCut DIA500 and DHA650
Ring Gear
PureCut DIA500 and DHA650
A ring gear is cut on a ring-shaped hardened steel rim; it is the large gear in the differential of an automobile that is driven by the propeller shaft pinion to transmit power to the live axle.
The material of choice for these components is case hardened steel. It is preferable to machine these parts in the hardened state to avoid deformations during the heat treatment process. Polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) was the enabling technology for hard part turning.
Element Six PureCut product range is recommended for this application. For machining operations with less interrupts DIA500 is recommended. For more interrupted machinng DHA650 is the ideal choice. Both grades are also available as solid integral inserts that allow for step-change reduction in cost per machining edge over backed materials.
 Pinion
PureCut DHA650
Pinion
PureCut DHA650
A pinion is a round, hardened steel gear; it is the smaller gear that meshes at an angle with the ring gear to transmit the power through the differential to the live axle.
The material of choice for these components is case hardened steel. It is preferable to machine these parts in the hardened state to avoid deformations during the heat treatment process. Polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) was the enabling technology for hard part turning.
Element Six PureCut grade DHA650 is recommended for this application offering tool life >50% over industry benchmark grades plus the ability to go to higher speeds for increased productivity. DHA650 is also available as solid integral inserts that allow for step-change reduction in cost per machining edge over backed materials.
 Camshaft
ABN800 / ABN900
Camshaft
ABN800 / ABN900
The camshaft is used to operate the intake and exhaust valves of an internal combustion engine. Due to the intimate relationship between the relative rotation of the crankshaft and camshafts, high tolerance grinding of the camshafts and cam lobes is required.
Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is the most suitable abrasive material for grinding of camshafts. However, the correct particle shape must be selected to survive the quick changes in material removal rates on the outer diameter of cam lobes. ABN800 and ABN900 are the optimal grain types fit for this challenging grinding operation.
 Crankcase
Aero-Dianamics™
Crankcase
Aero-Dianamics™
The engine cylinder block, or crank case, houses hundreds of parts and constitutes 20 - 25% of the total weight of the engine. Typically cast from Aluminum alloys, many finish machining operations are required, such as drilling, reaming and tapping.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) cutting tool materials are able to accomplish all of these operations, offering flexible and effective solutions for high output production lines.
PCD’s extreme hardness provides a cutting tool with exceptional wear resistance that can be run at faster machining speeds than carbide tools. This provides significant economic benefits through reduced tool changes, less production downtime and faster operations.
Element Six’s PCD Metal grades offer high tool life in both interrupted cutting operations such as milling, and in continuous operations such as reaming.
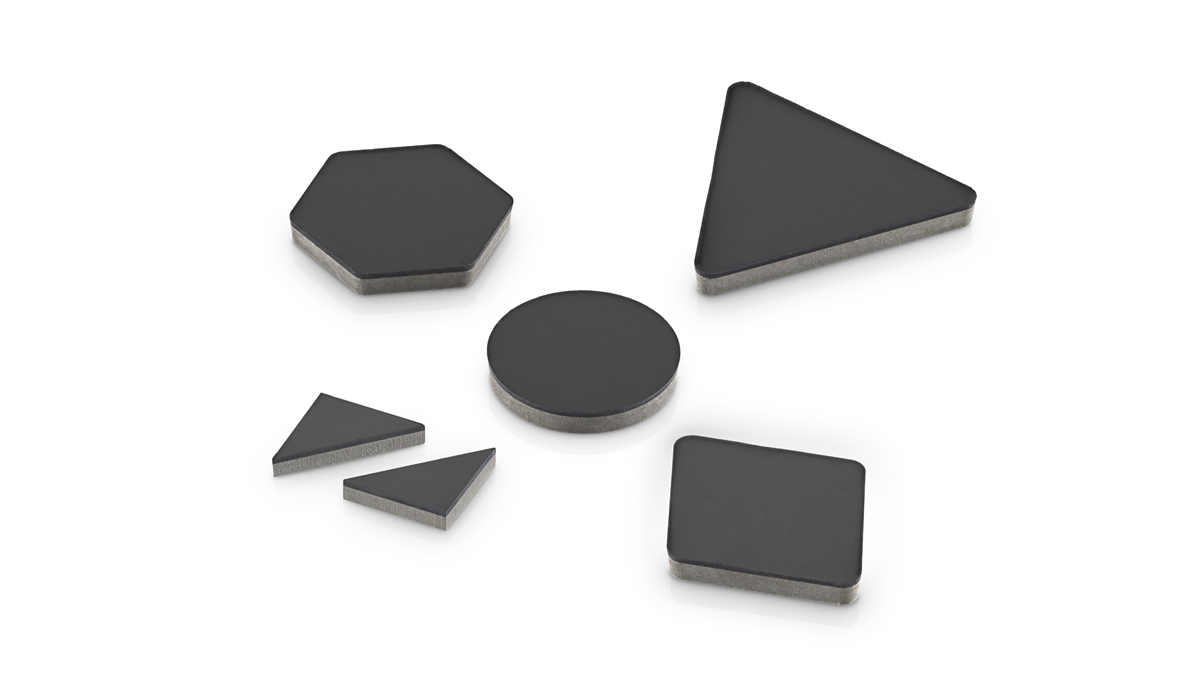 Crankcase
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Crankcase
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
The engine cylinder block, or crank case, houses hundreds of parts and constitutes 20 - 25% of the total weight of the engine. Typically cast from Aluminum alloys, many finish machining operations are required, such as face milling, pocket milling and boring.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) cutting tool materials are able to accomplish all of these operations, offering flexible and effective solutions for high output production lines.
PCD’s extreme hardness provides a cutting tool with exceptional wear resistance that can be run at faster machining speeds than carbide tools. This provides significant economic benefits through reduced tool changes, less production downtime and faster operations.
Element Six’s PCD Metal grades offer high tool life in both interrupted cutting operations such as milling, and in continuous operations such as reaming.
 Crankshaft
ABN800
Crankshaft
ABN800
The crankshaft is a solid hardened steel shaft which converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into a rotational motion used to drive the gearbox and thus the wheels of a car.
Due to high rotational speed, the crankshaft must be ground to high tolerances to reduce unwanted vibration.
Element Six cubic boron nitride (CBN) products such as ABN800 offer significant benefits over conventional grits in crankshaft grinding.
 Cylinder Liner
DBS900
Cylinder Liner
DBS900
With the increasing drive for efficiency gains within the Automotive industry, significant efforts target power-to-weight gains within the engine.
Aluminium alloys offer significant weight advantages over cast iron, as well as having a higher thermal conductivity. A wear-resistant coating is still required inside the cylinder bore and so technology has progressed to allow, typically, an iron-based coating to be applied around 0.2 - 0.3mm thick. This coating is then machined to the required thickness.
Where this machining was previously the expensive process of honing, Element Six’s PCBN materials offer a more economical option to bore the liner using defined edge cutting tools. This benefits the end user with faster machining times, utilisation of cheaper machines within the production line and a more controllable process.
 Valves
ABN900
Valves
ABN900
Valves are used in most piston engines to open and close the intake and exhaust ports in the cylinder head.
Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is the most suitable abrasive material for grinding valves which are typically made of nickel chromium alloy steels.
Using electroplated tools in the grinding process enables high material removal rates and high productivity. Element Six ABN900 is the perfect choice, offering an improved grinding process through a combination of uniform shape and good bond retention. Its controlled breakdown generates lower forces, allowing even higher material removal rates, whilst the wear resistance of the grit enables long grinding times and high productivity.
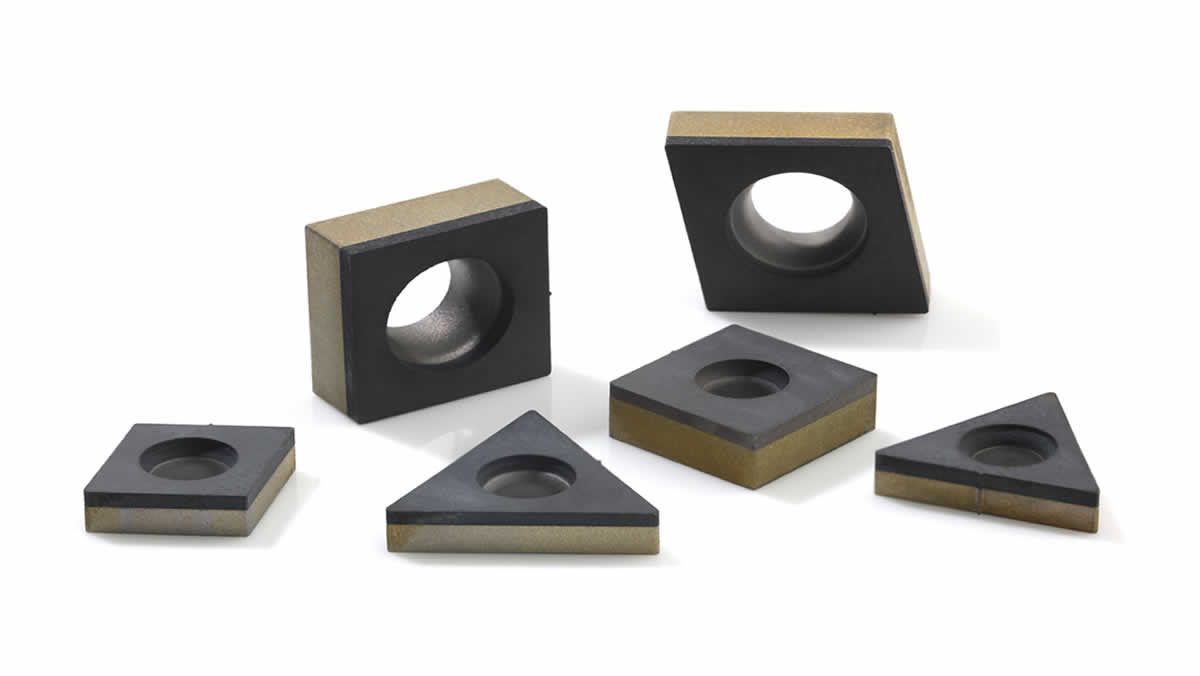 Valve Seats
DBS900 and PureCut DIA500
Valve Seats
DBS900 and PureCut DIA500
The valve seat is the surface against which an exhaust valve rests when that valve is closed.
Made from Powder Metal (PM) material, different operations are performed to generate conical-section surfaces into the valve seat. As PM is difficult to machine, polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) tools are the most suitable material for valve seat machining.
Due to the broad range of PM materials, the selection of the best PCBN grade for a given application should be made only after material analysis.
 Alloy Wheels
PCD Metal – CMX850
Alloy Wheels
PCD Metal – CMX850
The use of Aluminum and/or Magnesium alloys for wheels was pioneered in the 1920’s motorsport scenes and is now used in the general market as a key styling element. It has the added performance benefits of reduced weight and greater stiffness over stamped steel wheels.
Typically cast in one piece, alloys offer the designer greater degrees of freedom. These near-net shape castings require finish machining to size and shape - utilising milling, drilling and turning operations.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is used extensively, primarily for its increased tool life which provides significant economic benefits in mass production. The latest styling elements, such as ‘diamond cut wheels’, utilise PCD’s superior cutting edge quality to produce exceptional surface finishes without the need for secondary polishing operations.
CMX850 provides a robust and economical solution, with enhanced processing for the tool manufacturer and remarkable cutting performance for the end user.
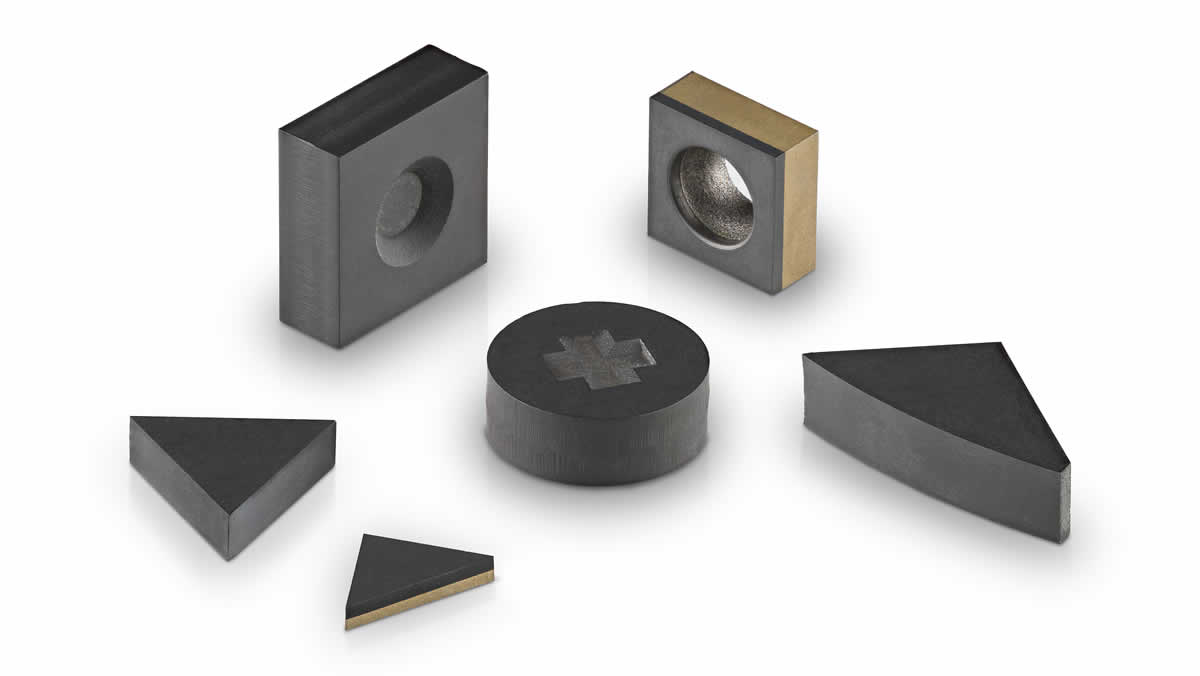 Brake Disc
AMB90, DBW85, AMK90
Brake Disc
AMB90, DBW85, AMK90
The disc brake employs callipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc in order to create friction that retards the rotation of an axle, either to reduce its speed or to stop.
Grey cast iron is relatively inexpensive and easy to produce. It has excellent thermal conductivity and stability at temperatures from 400° to 600°C.
The machinability of Grey cast iron is significantly improved using polycrystalline boron nitride (PCBN) where the high speeds achievable generate a protective layer on the tool resulting in extreme tool life.
 Suspension Components
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Suspension Components
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Reducing weight is a key issue in the drive for greater vehicle efficiency. Previously, typical suspension components were made from pressed steel for ease of manufacture, but the industry is now moving towards pressed, cast or machined Aluminum.
Element Six can provide a full spectrum of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) grades offered in large diameter, high yield formats to fit the application. The Syndite range of PCD offers the greatest performance option for Aluminum milling, boring and drilling.
 Suspension Components
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Suspension Components
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Reducing weight is a key issue in the drive for greater vehicle efficiency. Previously, typical suspension components were made from pressed steel for ease of manufacture, but the industry is now moving towards pressed, cast or machined Aluminum.
Element Six can provide a full spectrum of polycrystalline diamond (PCD) grades offered in large diameter, high yield formats to fit the application. The Syndite range of PCD offers the greatest performance option for Aluminum milling, boring and drilling.
 Tyres
MD111
Tyres
MD111
Steel wire cords, beads and belts are key components of a tyre, holding the tyre onto the rim of the wheel. They provide the tyre’s strength and maximise the tyre’s contact patch with the road.
Wire drawing is a metalworking process used to reduce the cross-section of a wire by pulling the wire through a single, or series of, drawing dies. There are many applications for wire drawing, including electrical wiring and cables.
Single crystal diamond wire drawing dies provide exceptional wear resistance and reduce hole wear distortion, delivering less down time, higher productivity and a high quality finish of drawn wire.
 Diamond Bearings
PCD
Diamond Bearings
PCD
Typically, bearings are used in many applications within a car, with multiple rotating shafts requiring precise control and movement. Bearing materials require high hardness, low coefficient of friction and good thermal stability.
Diamond offers exceptional performance in all three of these properties and maintains high tolerance sizes for bearings to run over their lifetime. Diamond bearings could dramatically increase component life as bearing surfaces are one of the first areas to wear.
Until now the opportunity has not been realised due to difficulties producing diamond in the required shapes and sizes. Element Six is at the forefront of diamond bearing innovation for the automotive industry.
 Hybrid Drive Train
CVD Heat Spreaders
Hybrid Drive Train
CVD Heat Spreaders
The growth and development of Hybrid and Electric vehicles is set to continue, increasing the electrification of drive train components - from motors and transmission to fuel injection, engine and knock control.
Within some of these electronic systems, heat spreaders are essential to prevent devices from overheating and malfunctioning. For example, inverters in Hybrid drive trains generate large amounts of heat when converting direct current from the batteries to an alternating current in order to power the motor.
Diamond has the highest room temperature thermal conductivity of any material. It is also electrically insulating with a high mechanical strength, low weight and chemically inert - making it the material of choice for high voltage power devices within the demanding environment of a vehicle drive train.
 Powertrain Sensors
Boron doped diamond
Powertrain Sensors
Boron doped diamond
The car of the future will have more embedded sensors to monitor the performance of the powertrain, be they combustion, electric or hybrid systems. Automotive sensors need to be simple, low cost and very reliable.
Electrochemical sensors could be used to control and monitor the performance of batteries and fuel cells. Modern combustion engines depend on sensors to manage combustion. Measurements that currently require specialist external instrumentation could be made within the vehicle itself, using new electrochemical sensors to monitor emissions.
Diamond is a semiconductor and can be doped with boron to give it metal-like electrical conductivity, whilst retaining diamond’s inert, robust characteristics. Diamond electrodes can be manufactured with the stability, range and sensitivity to enable new types of simple electrochemical sensors to be developed.
 Safety Sensors
Optical grade CVD Diamond
Safety Sensors
Optical grade CVD Diamond
Multiple imaging systems that can operate at different wavelengths are able to enhance driver safety aids. Multispectral imaging such as infrared night vision and millimetre wave imaging (as used in airport scanners) can greatly enhance safety in poor visibility conditions.
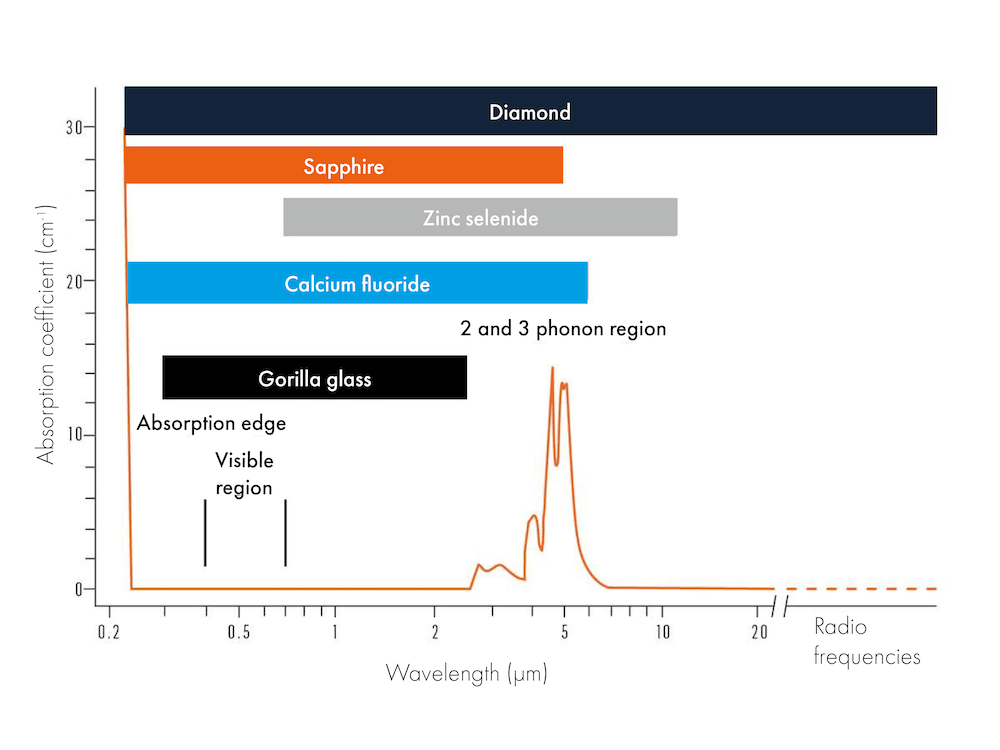
Diamond is an unparalleled multispectral optical material with a window spanning from the deep UV through to the visible, infrared and millimetre wave bands. It is also an extremely robust material that lends itself well to being the protective window. Future delicate multispectral sensor technology can be deployed behind a multi spectral diamond precision optical that will protect it from the environment for the lifetime of the car.
 Aluminum parts
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Aluminum parts
PCD Metal – CMX850, CTB004, CTM302
Aluminum is already used in structural components throughout the chassis of commercial vehicles to reduce sprung weight. With the drive for ever greater efficiency and improved performance, its use is set to increase. Lighter Aluminum components in areas such as the hub carrier, upright suspension arms, control arms and wheels will make them more easily controlled by the chassis and shock absorber - improving performance and aiding overall economy.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) presents unrivalled cutting tool performance in high Silicon content Aluminum alloys. Element Six can provide a full spectrum of PCD grades offered in large diameter, high yield formats for complex geometry tools to fit the application. The Syndite range of PCD offers the greatest performance option for Aluminum milling, boring and drilling.
 Ceramic and MMC Brake discs
CMX850
Ceramic and MMC Brake discs
CMX850
The ideal brake disc would be light weight with high abrasion resistance, high compressive strength and good thermal conductivity in order to reduce vehicle weight and increase overall performance. Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) fit these combined requirements. These materials typically combine an Aluminum alloy as the matrix, with a hard phase material as the strengthening component.
However, MMCs are incredibly difficult to machine efficiently. Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is one of the few cutting tool materials that offers economical cutting performance of MMC, in turning and drilling applications. Where Tungsten Carbide offers a tool life of minutes, PCD can perform for hours.
With our Syndite range of discs for turning applications and the Aero-Dianamics round tools for drilling, Element Six offers the best solutions to tackle the machining operations of MMC materials.
 Ceramic and MMC Brake discs
Aero-Dianamics™
Ceramic and MMC Brake discs
Aero-Dianamics™
The ideal brake disc would be light weight with high abrasion resistance, high compressive strength and good thermal conductivity in order to reduce vehicle weight and increase overall performance. Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs) fit these combined requirements. These materials typically combine an Aluminium alloy as the matrix with a hard phase material as the strengthening component.
However, MMCs are incredibly difficult to machine efficiently. Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is one of the few cutting tool materials that offers economical cutting performance of MMC, in turning and drilling applications. Where Tungsten Carbide offers a tool life of minutes, PCD can perform for hours.
With our Syndite range of discs for turning applications and the Aero-Dianamics round tools for drilling, Element Six offers the best solutions to tackle the machining operations of MMC materials.